Concepts Clarification¶
Granovette's theory
- Weak tie (socially weak, but structually important for information flow) \(\leftarrow\) Strength \(\to\) Strong tie (socially strong, but heavily redundant in terms of information access)
- Bridge: if removed leads to disconnected graph; Local Bridge: edges of span \(\gt 2\), span is the distance of the edge endpoints if the edge is deleted
- Tradic Closure: two strong ties \(A-B\), \(A-C\), imply a third edge \(B-C\) (can be either strong or weak)
- Local Bridges and Weak Ties:
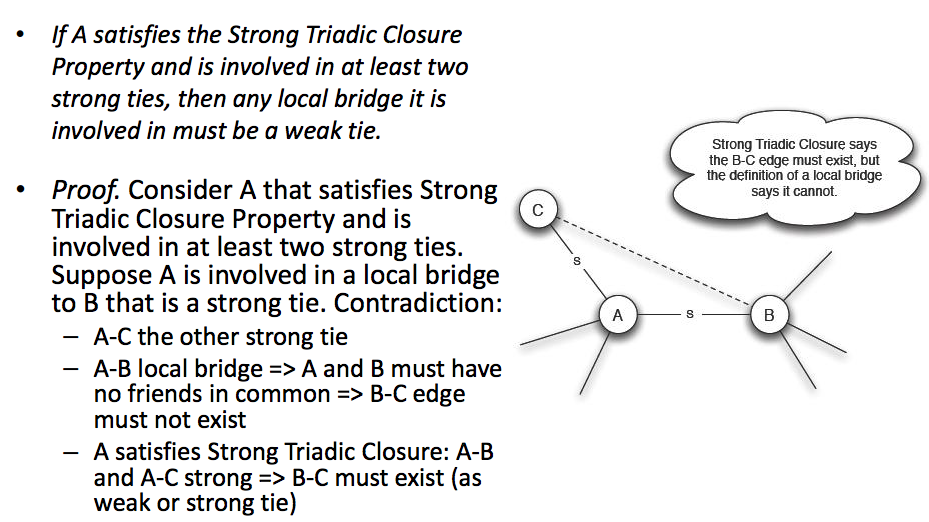 The reason why \(A\) should be involved in at least \(2\) strong ties is because if \(A\) only has one strong tie, that strong tie itself could be a local bridge and it does not violate tradic closure assumption
The reason why \(A\) should be involved in at least \(2\) strong ties is because if \(A\) only has one strong tie, that strong tie itself could be a local bridge and it does not violate tradic closure assumption - Edge Overlap: \(O_{ij} = \frac{N(i)\bigcap N(j)}{N(i)\bigcup N(j)}\), where \(N(i)\) are the neighbors of node \(i\) (not include \(j\)), the endpoints of a local bridge have no common neighbor, therefore overlap is 0
- In cell-phone network, highly used (strong) links has high overlap (strong locality)
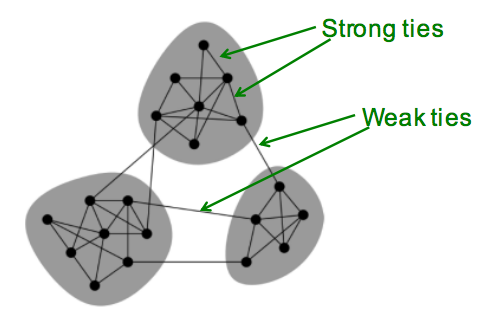
- Keep this picture in mind:
Burt's theory
- Structural Hole: To understand what does it mean
- Understand the importance of bridging role / middleman / broker.
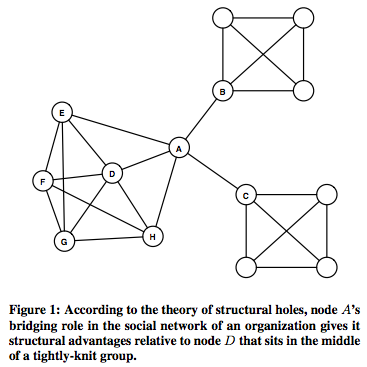
- Information within clusters tends to be rather homogeneous and redundant. Non-redundant information is most often obtained through contacts in different clusters. When two separate clusters possess non-redundant information, there is said to be a structural hole between them. Structural hole is lack of connection between two nodes that is bridged by a broker.
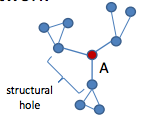
- Since individuals can benefit from serving as intermediaries between others who are not directly connected, this leads to Strategic Network Formation which studies the evolution of network when individuals in a social network have incentives to form links that bridge otherwise disconnected parties. Check the following talk, if you only want to know what is structural hole, check the first 15 minutes; if you are interested in applying game theoretical model on strategic network formation problem, check the full video
- Understand the importance of bridging role / middleman / broker.
In [1]:
from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo
YouTubeVideo('yEY9_HwvnqU')
Out[1]:
- Network Constraint: It is one metric to find bridgers (other metrics can be betweenness centrality .e.g). An individual's network constraint measures the extent to which he links to others that are already linked to each other. Low network constraint means that an individual has links to others who are not already linked to each other. High betweenness centrality and low network constraint both indicate bridging. How to calculate network constraint? \[p_{ij} = \frac{w_{ij}}{\sum_{j\in N(i)}{w_{ij}}}\] \(w_{ij}\) is the weight of edge \(e_{ij}\) (.e.g 1 for strong tie, 0.5 for weak tie), \(p_{ij}\) indicates how much time/energy \(i\) spends on \(j\), with this definition of \(p_{ij}\), the network constraint of \(i\) is defined as \[C_i = \sum_{j\in N(i)}{c_{ij}} = \sum_{j\in N(i)}[p_{ij} + \sum_{k\in N(i)}(p_{ik}p_{kj})]^2\]
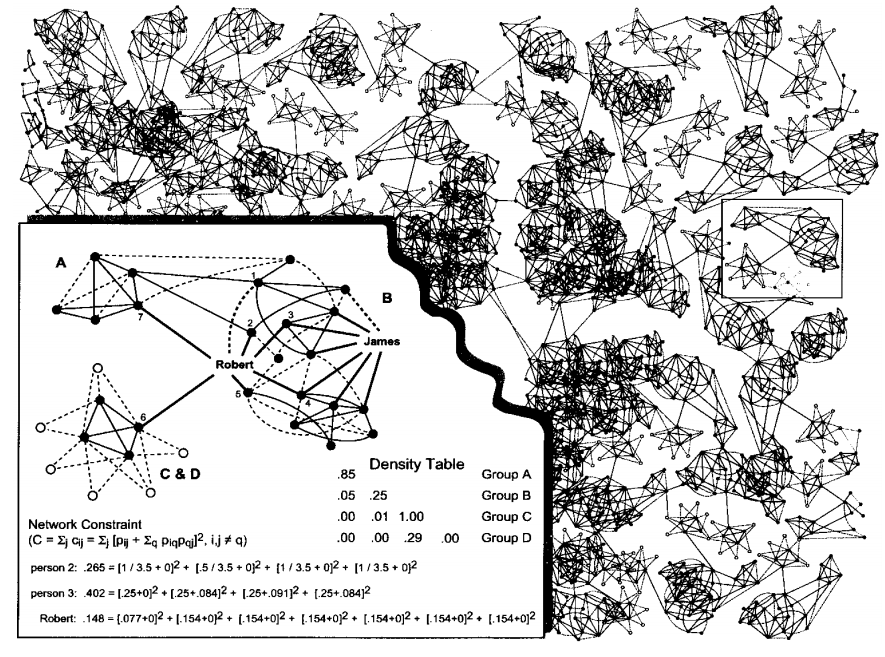 In the above picture, for person 2 and Robert, there is no links among their neightbors, for person 3, there is triangulars among him and his neighbors. So low constraint \(\Rightarrow\) contacts are disconnected, high constraint \(\Rightarrow\) contacts are close
In the above picture, for person 2 and Robert, there is no links among their neightbors, for person 3, there is triangulars among him and his neighbors. So low constraint \(\Rightarrow\) contacts are disconnected, high constraint \(\Rightarrow\) contacts are close
Community Detection
- Betweenness
- Definition: node/edge betweenness is the number of shortest paths between pairs of nodes that path through the node/edge
- Algorithm for calculation of betweenness (Brandes' algorithm, for unweighted graph ):
 \(d[w]\) is the distance to the root node \(s\), \(P[w]\) saves the parent nodes of node \(w\), \(\sigma[w]\) is the number of shortest paths from root node \(s\) to node \(w\); \(\delta[w]\) is used to accumulates the weighted flow from its children nodes and also distributes it to its parent nodes(.e.g \(v\)) with weight \(\sigma[v] / \sigma[w]\); \(C_B\) is the node betweenness centrality.
\(d[w]\) is the distance to the root node \(s\), \(P[w]\) saves the parent nodes of node \(w\), \(\sigma[w]\) is the number of shortest paths from root node \(s\) to node \(w\); \(\delta[w]\) is used to accumulates the weighted flow from its children nodes and also distributes it to its parent nodes(.e.g \(v\)) with weight \(\sigma[v] / \sigma[w]\); \(C_B\) is the node betweenness centrality.
- Girvan-Newman algorithm: progressively removing edges from the original network \(\to\) dendrogram
Modularity
- Definition: from Wiki: Modularity: one measure of the structure of networks or graphs, measure the strength of division of a network into modules (also called groups, clusters or communities). Networks with high modularity have dense connections between the nodes within modules but sparse connections between nodes in different modules.
- How to turn a given graph (.e.g in total \(n\) nodes where each node \(i\) has degree \(k_i\), and \(m\) edges) into a random graph and still keep the degree of each node unchanged? Concept of configuration models is a randomized realization of a particular network: cuts each edge into two halves, and then each half edge, called a stub, is rewired randomly with any other stub in the network even allowing self loops (multigraph). In this way, the total number of stubs is \(\sum_{i}k_i = 2m\), the probability of choosing any stub from node \(j\) is \(\frac{k_j}{2m}\), the expected number of edges between \(i\) and \(j\) in the completely random graph will be \(\frac{k_ik_j}{2m}\)
- For a Graph \(G\), define modularity \(Q(G,S)\) with respect to a community partition \(S\) as \[Q(G,S) = \frac{1}{2m} \sum_{s\in S}\sum_{i,j\in s}[A_{ij}-\frac{k_ik_j}{2m}] = \sum_{i,j}[\frac{A_{ij}}{2m} - \frac{k_ik_j}{4m^2}]\delta(c_i,c_j)\] \(A\) is adjacency matrix, \(c_i\) is the community index which \(i\) belongs to in partition \(S\), \(\delta(c_i,c_j) = 1\) when \(c_i = c_j\), otherwise 0
- Modularity Matrix formulation: define \(Z_{ir}\) to be 1 if \(c_i = r\) and zero otherwise, then \(Z\) is a \(n \times |S|\) matrix (membership matrix, each row \(Z_{i\bullet}\) is a length \(|S|\) membership vector for node \(i\)), so \[\delta(c_i, c_j) = \sum_rZ_{ir}Z_{jr}\] \[Q(G,S) = \frac{1}{2m} \sum_{i,j}\sum_{r} [A_{ij} - \frac{k_ik_j}{2m}]Z_{ir}Z_{jr} = \frac{1}{2m}Tr(Z^TBZ)\] \(B\) is called modularity matrix with \(B_{ij} = A_{ij} - \frac{k_ik_j}{2m}\)
- Goal: maximize modularity, with this goal come with different community detection algorithms, for those who are interested check this slides
Practical Skills¶
Gephi
NetLogo
Be sure to check the Syllabus of Lada Adamic's course @ coursera, there are many netlogo models provided there for you to play with, don't miss the funny part of this course.